Electroactive Polymers (EAPs)
Pushing the limits: ELASTOSIL® Film
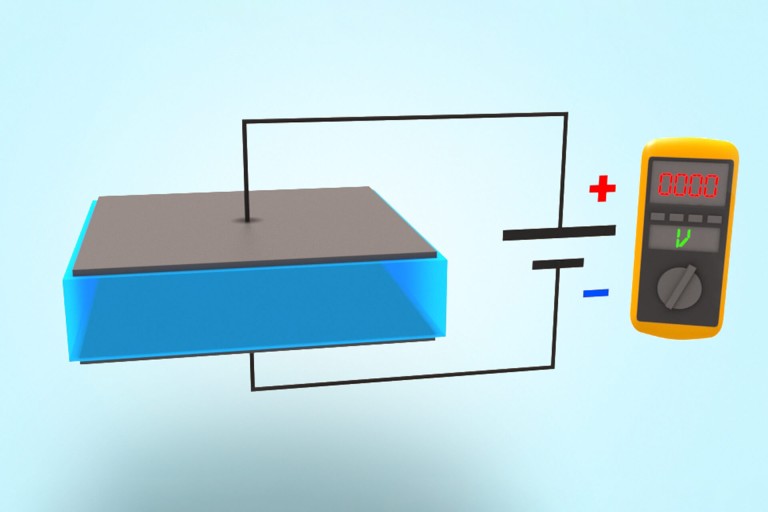
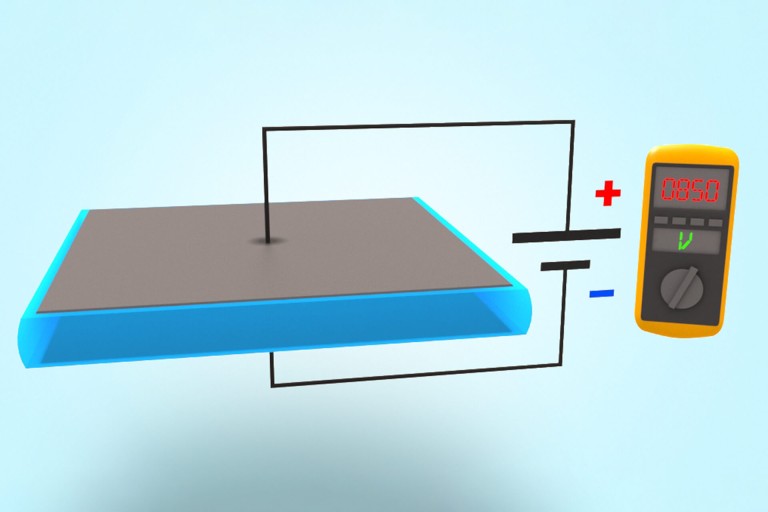
Electroactive polymers are materials that have been modified in such a way that they can convert electrical impulses into mechanical movement – a principle that enables the production of capacitive sensors, actuators and generators. Its NEXIPAL ® and ELASTOSIL ® Film products give WACKER an active presence on this market.
Sensors

Intelligent sensors measure changes in capacitance and thus record expansive and compressive movements. NEXIPAL ® sensors made from ELASTOSIL ® Film are extremely thin and flexible, making them ideal for smart textiles and recording body movements in medical, athletic and lifestyle applications. In addition, NEXIPAL ® sensors are perfectly suited to environments with a variety of temperature demands.
Actuators
NEXIPAL ® Act – components made from ELASTOSIL ® Film and flexible electrodes – are used in the field of actuator technology, where they show considerable potential for saving energy and weight relative to conventional technologies. Applications include valves, pumps, relays, artificial muscles, grippers and sound systems.
Other benefits include:
Generators
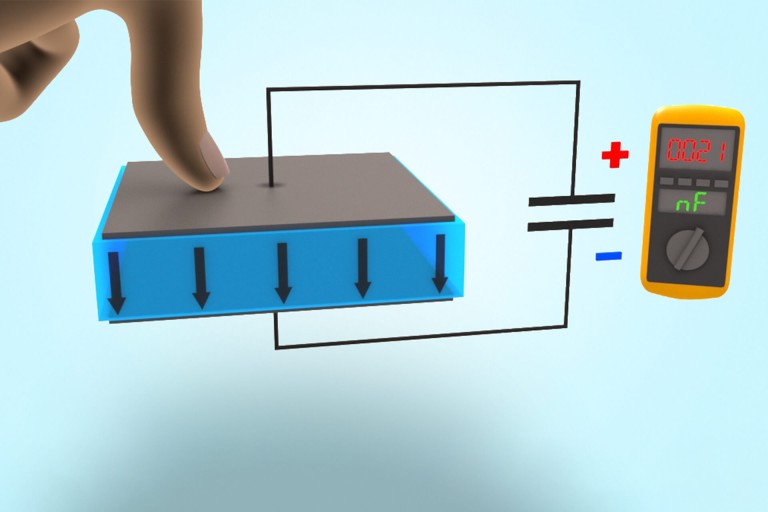
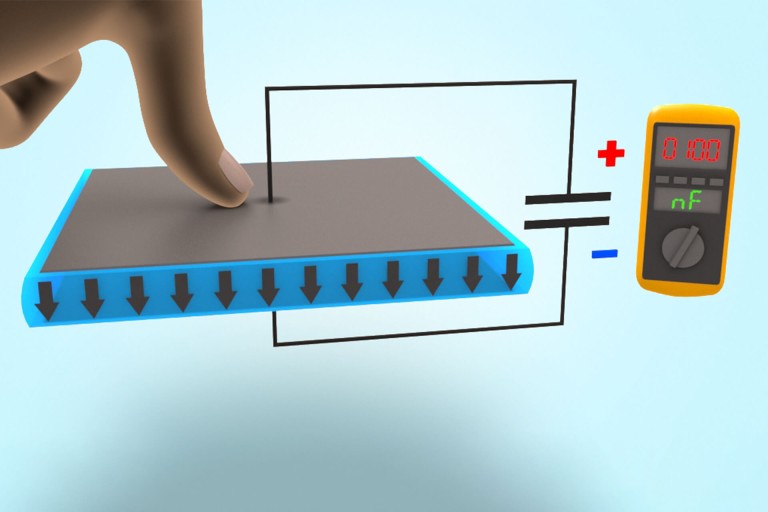
Here, the mode of operation is the opposite of that for actuators. In this case, NEXIPAL ® components made from ELASTOSIL ® Film and flexible electrodes are used for converting mechanical work into electrical energy. This enables novel, environmentally friendly energy-generation systems such as tidal power plants.
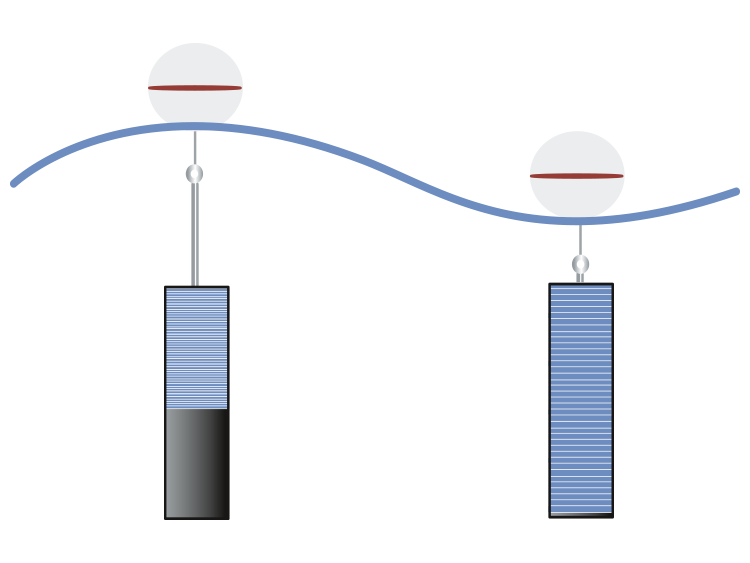
A buoy is connected to a generator consisting of NEXIPAL ® laminates made from ELASTOSIL ® Film and suitable electrode material.